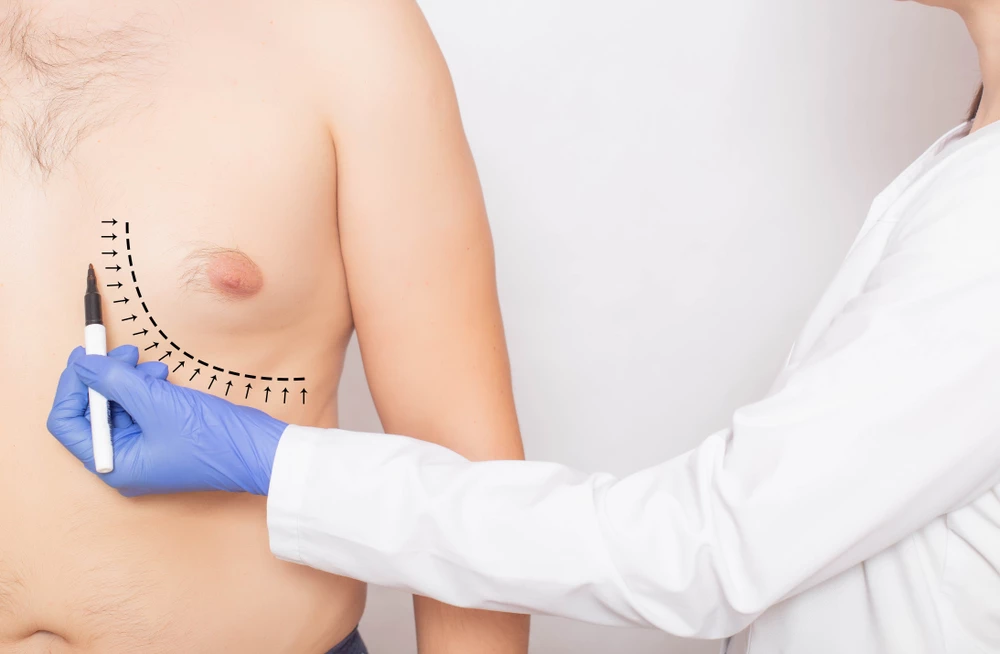
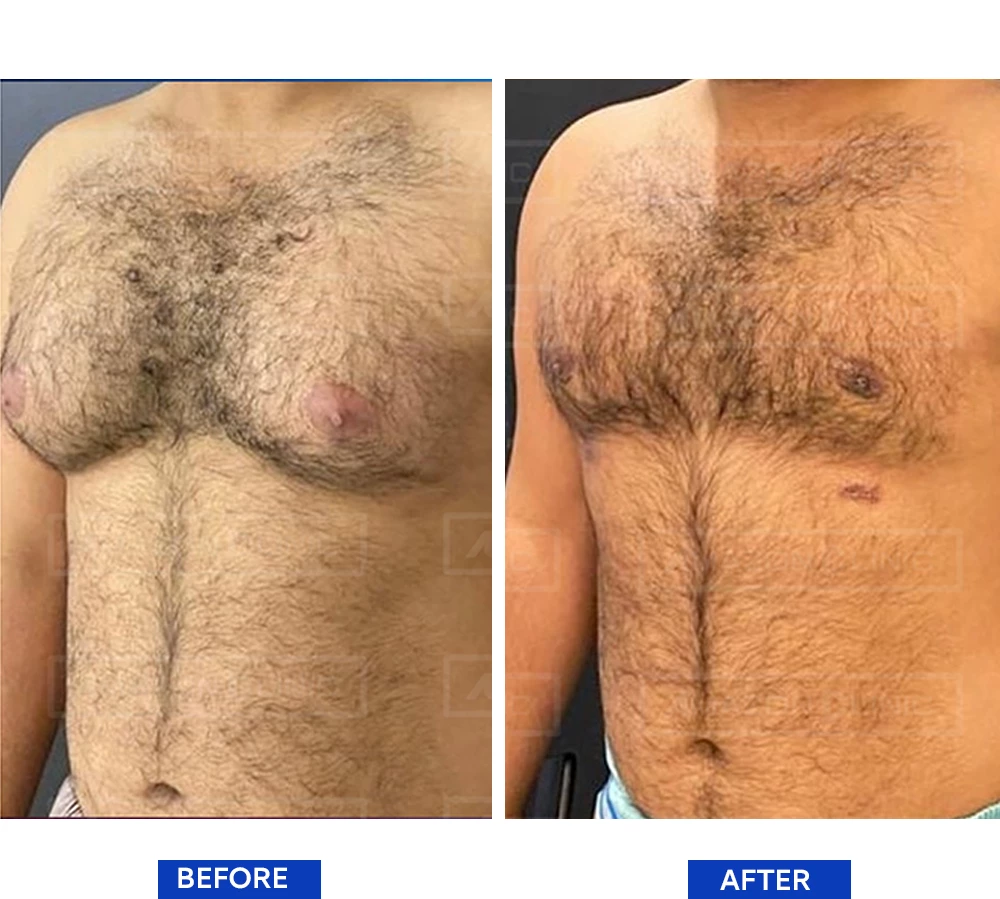
Gynecomastia is a condition in which there is an abnormal growth of breasts in men, and it can occur for several reasons, including:
- Hormonal changes: This is when there is an imbalance in the hormones in a man's body, such as an increase in the level of the female hormone (estrogen) and a decrease in the level of the male hormone (testosterone).
- Medications: Some medications for chronic diseases can cause Gynecomastia in men, such as hormonal medications like estrogen, progesterone, and corticosteroids, anti-tumor chemicals and hormones, anti-seizure medications like valproate and carbamazepine, anti-fungal medications like Ketoconazole and Itraconazole, and anti-hypertensive medications like Captopril and Enalapril, as well as anti-depressant medications like fluoxetine and sertraline.
- Chronic diseases: Some chronic diseases like liver disease, diabetes, and hormonal disorders can cause Gynecomastia in men.
- Genetic factors: There may be a family history of Gynecomastia in the affected man.
- Obesity: Obesity can increase the likelihood of Gynecomastia in men, as fat is stored in the body and can affect hormone levels in the body.
- Psychological stress: Psychological stress can cause a disruption in hormone balance, which may lead to Gynecomastia.