8 organs in your body you can live without!
In many action movies, we have seen how the hero gets stabbed with a knife, shot in the abdomen, or experiences an accident that causes the loss of one of their limbs, yet they miraculously survive! This may seem somewhat fantastical, but in reality, it can be logical because the hero is human, and humans can live without 8 organs out of a total of 78 vital organs and tissues in their body.
Translation: In many action movies, we have seen how the hero gets stabbed with a knife, shot in the abdomen, or experiences an accident that causes the loss of one of their limbs, yet they miraculously survive! This may seem somewhat fantastical, but in reality, it can be logical because the hero is human, and humans can live without 8 organs out of a total of 78 vital organs and tissues in their body.
What are the organs that a human can live without?
1- Appendix:
The appendix is a small organ in the digestive system, located in the lower abdomen on the right side of the colon. Its length typically ranges from 5 to 10 centimeters. Although the exact function of the appendix is not fully understood, it is believed to play a role in the immune system and housing beneficial bacteria in the digestive system.
However, the appendix can become inflamed in a condition known as appendicitis, which is a medical emergency that usually requires surgical removal. According to statistics, approximately 7% of adults experience appendicitis.
2- Wisdom Teeth (Third Molars):
The prevailing belief is that wisdom teeth are associated with wisdom itself, and those who haven't grown them yet are still immature. However, this belief is entirely inaccurate. The reason they are called "wisdom teeth" is that they typically erupt much later than the other teeth, usually between the ages of 17 and 25 when a person has reached adulthood.
Humans have four wisdom teeth located at the back of the mouth, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower jaw. However, not all individuals have all four wisdom teeth. It is possible for one or two or even none of the wisdom teeth to emerge, or they may be completely impacted.
The presence of wisdom teeth in the back of the mouth makes them difficult to clean, which puts them at risk of decay and damage. This can also cause damage to the surrounding teeth. If wisdom teeth are affected by damage, inflammation, or decay, they should be extracted promptly to avoid impacting other teeth and gums. Living without wisdom teeth is possible, and individuals can adapt to their absence.
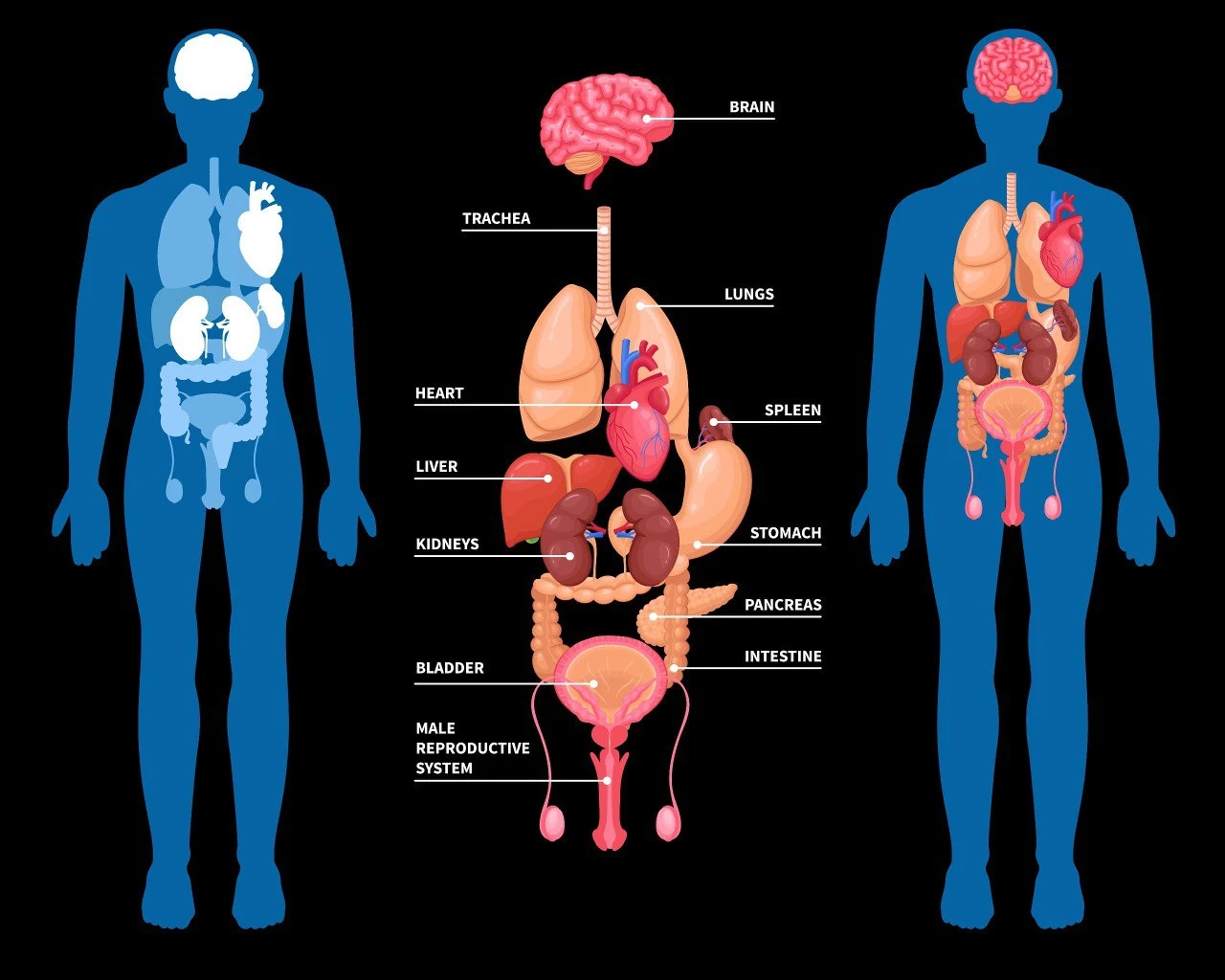
3- Spleen:
Located on the left side of the abdomen, in the back, below the ribs, you will find this organ with distinctive colors. It has a dark red color and small white pockets. The red color is responsible for storing and recycling red blood cells, while the white color is associated with storing white blood cells and platelets.
You can live comfortably without a spleen. This is because the liver plays a role in recycling red blood cells and their components. However, it is necessary to receive vaccinations to protect against bacteria that the spleen would typically help defend against if it is removed.
4- Stomach:
The stomach is sometimes surgically removed due to cancer, tumors, or trauma. In 2012, a British woman had her stomach removed after ingesting a cocktail containing liquid nitrogen.
When the stomach is removed, the surgeon connects the esophagus directly to the small intestine, and after that, it is possible to consume a normal diet with the use of vitamin supplements.
5- Reproductive Organs:
In the female reproductive organs, there are two ovaries, and one or both of them, as well as the uterus, can be removed due to cancer or tumors.
In the male reproductive organs, there are two testes, and one of them can be removed in cases where an individual experiences trauma due to sports, accidents, or violence. Afterward, the person can still reproduce with one testis.
6- Colon:
The colon is a tube-like organ that is approximately six feet long. Its main functions are water absorption and the formation of stool through its solidification. It can be affected by cancer or other diseases that may require the removal of a portion or the entire colon.
Most people recover well after this surgery, but it is recommended to follow a diet consisting of soft foods to aid in the healing process, and then gradually transition to a diet that is suitable for the changes that have occurred in the intestines.
7- Gallbladder:
The gallbladder is located beneath the liver on the upper right side of the abdomen, below the ribs. It stores a substance called bile. Bile is continuously produced by the liver to aid in the digestion of fats, but when not in use, it is stored in the gallbladder.
If the cholesterol levels in the bile increase, gallstones can form in the gallbladder, and a person may need to have their gallbladder removed.
There are some symptoms that a person may experience after gallbladder removal, such as indigestion and gas buildup in the abdomen, but overall, they can live normally without it.
8- Kidneys:
Each person has two kidneys, but they can live with one kidney. This can happen if they experience kidney failure that requires the removal of one kidney or if they choose to donate one of their kidneys to someone else.
The role of the kidneys is to filter the blood and maintain the balance of water and acids in the body. They act like filters that purify the blood, removing waste products, excess proteins, cells, and nutrients that the body needs. These waste products are then eliminated from the body through urine.
The human body is unbelievably resilient, capable of adapting to the loss of one or even multiple organs. For instance, if you donate a full liter of blood, along with approximately 3 trillion red blood cells, your body can regenerate them quickly.
The organs that humans can live without and still remain in good health
